 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DP00153: GTPase HRas |  |
| General information | |
| DisProt: | DP00153 |
| Name: | GTPase HRas |
| Synonym(s): | RASH_HUMAN Transforming protein p21 p21ras H-Ras-1 c-H-ras Ha-Ras GTPase HRas, N-terminally processed [cleavage product 1] |
| First appeared in release: | Release 1.1 (12/01/2003) |
| UniProt: | P01112 |
| UniGene: | Hs.37003 |
| SwissProt: | RASH_HUMAN |
| TrEMBL: | |
| NCBI (GI): | 131869 |
| Source organism: | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Sequence length: | 189 |
| Percent disordered: | 33% |
| Homologues: | |
| Native sequence |
|
| Functional narrative |
Hras, a member of the ras GTPase family, is a regulator of the RAS protein signal transduction pathway. It functions as a switch that contributes the regulation of cellular growth and differentiation by interacting with and hydrolyzing GTP. Once bound to a molecule of GTP, Hras is indirectly influenced by GTPase activating proteins (GAPS), and GTPase, which hydrolyzes GTP. GDP is then released by Hras due to its interaction with guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). When inactive, Hras can be found in the cytosol. However, when activated, Hras will migrate toward the golgi apparatus or plasma membrane of the cell. The disordered regions of Hras each interact with various proteins, including GTP, by altering their conformation in order to accommodate the interacting molecule. |
| Map of ordered and disordered regions | |
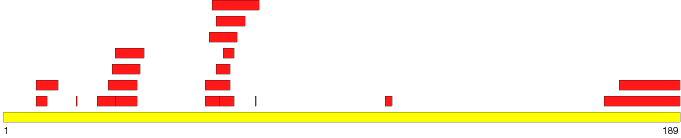  Note: 'Mouse' over a region to see the start and stop residues. Click on a region to see detailed information. | |
| Region 1 | |
| Type: | Disordered - Extended |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 10 - 13 |
| Length: | 4 |
| Region sequence: | GAGG |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 2 | |
| Type: | Disordered - Extended |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 10 - 16 |
| Length: | 7 |
| Region sequence: | GAGGVGK |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 3 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 21 - 21 |
| Length: | 1 |
| Region sequence: | I |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 4 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 27 - 32 |
| Length: | 6 |
| Region sequence: | HFVDEY |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 5 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 30 - 38 |
| Length: | 9 |
| Region sequence: | DEYDPTIED |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1CRP:A, 1CRQ:A, 1CRR:A, 1Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 6 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 31 - 39 |
| Length: | 9 |
| Region sequence: | EYDPTIEDS |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1AA9:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 7 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 32 - 38 |
| Length: | 7 |
| Region sequence: | YDPTIED |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 8 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 32 - 40 |
| Length: | 9 |
| Region sequence: | YDPTIEDSY |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 9 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 57 - 61 |
| Length: | 5 |
| Region sequence: | DTAGQ |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 10 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 57 - 64 |
| Length: | 8 |
| Region sequence: | DTAGQEEY |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1AA9:A, 1IOZ:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 11 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 58 - 66 |
| Length: | 9 |
| Region sequence: | TAGQEEYSA |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1AA9:A, 1CRP:A, 1CRQ:A, 1CRR:A, 1IOZ:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 12 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 59 - 72 |
| Length: | 14 |
| Region sequence: | AGQEEYSAMRDQYM |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 121P:A, 1P2U:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 13 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 60 - 64 |
| Length: | 5 |
| Region sequence: | GQEEY |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 4Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 14 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 60 - 68 |
| Length: | 9 |
| Region sequence: | GQEEYSAMR |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1Q21:A, 6Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 15 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 61 - 65 |
| Length: | 5 |
| Region sequence: | QEEYS |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1Q21:A, 6Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 16 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 62 - 65 |
| Length: | 4 |
| Region sequence: | EEYS |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 1Q21:A, 6Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 17 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 71 - 71 |
| Length: | 1 |
| Region sequence: | Y |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 18 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 107 - 109 |
| Length: | 3 |
| Region sequence: | DDV |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Function arises via a disorder to order transition |
| Functional classes: | Molecular recognition effectors |
| Functional subclasses: | Protein-protein binding |
Detection methods:
| |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 19 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 168 - 189 |
| Length: | 22 |
| Region sequence: | LRKLNPPDESGPGCMSCKCVLS |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | 4Q21:A |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Region 20 | |
| Type: | Disordered |
| Name: | |
| Location: | 172 - 189 |
| Length: | 18 |
| Region sequence: | NPPDESGPGCMSCKCVLS |
| Modification type: | Complex Engineered Fragment |
| PDB: | |
| Structural/functional type: | Relationship to function unknown |
| Functional classes: | Unknown |
| Functional subclasses: | Unknown |
| Detection methods: | |
References:
| |
| Comments: | |
| Comments | |
|
| If you have any comments or wish to provide additional references to this protein or its disordered region(s), please click here to e-mail us. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|